Grammar rules: future tenses in English
The following article is the third one in the series about “Tenses in English”. We have already spoken about Present and Past tenses in English. We are going to learn grammar rules of future tenses in the English language. We all know that the future tenses in English is a grammatical category, which describes the event that will occur in future, after the conversation.
How to form Future tense in English?
If we take a look at the list of tenses in English we will see that Future Tense is presented in 4 forms: Future Simple, Future Continuous, Future Perfect and Future Perfect Continuous. Two last tenses are used very rarely.
Future Tenses are simple and easily formed. The most widespread tenses that express the future are Future Simple and Future Continuous. The main difference between them is that Future Continuous describes a long-lasting action unlike Future Simple expresses temporary action.
FORM
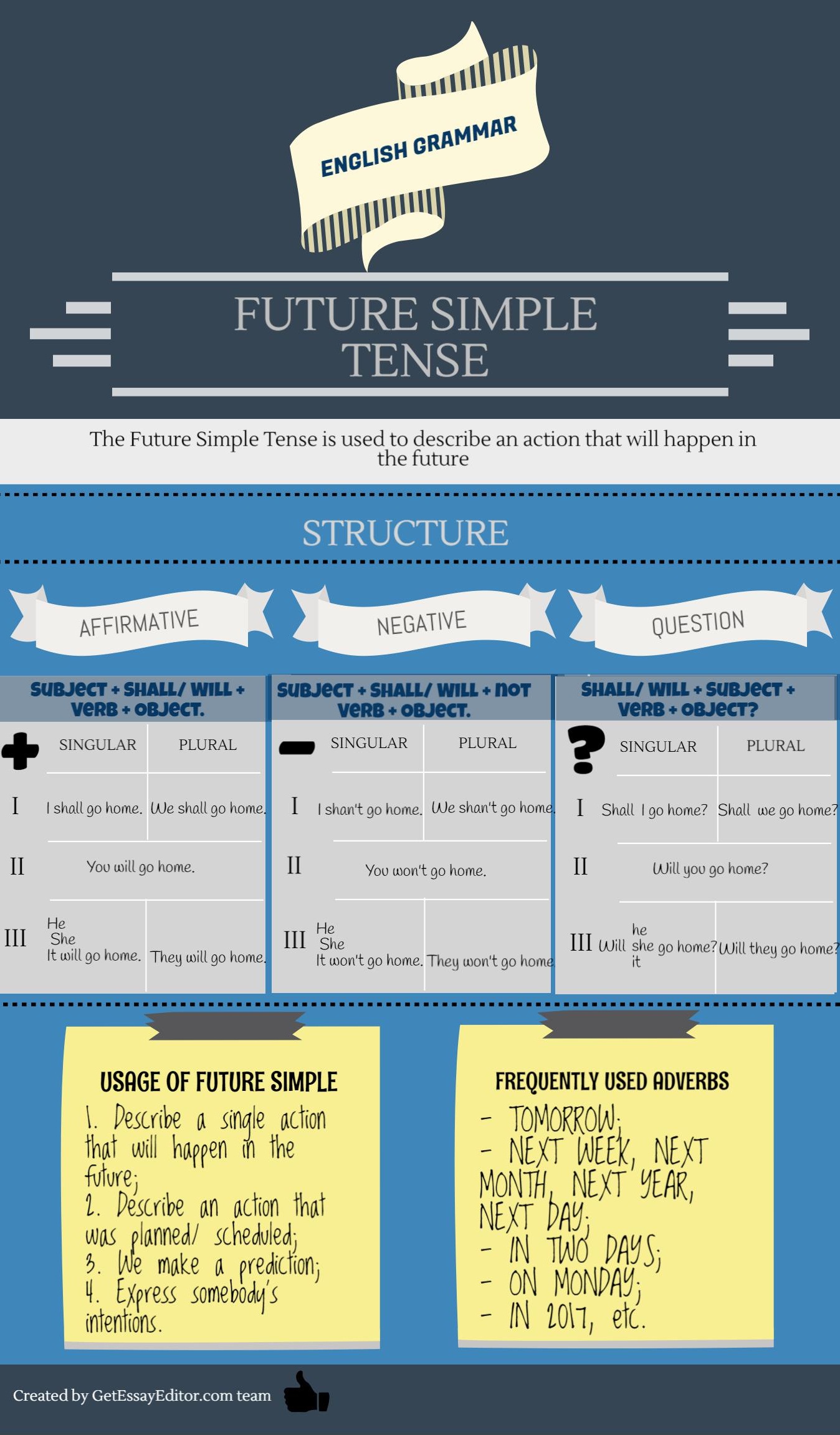
To create a sentence in Future Simple, we need to remember only two auxiliary verbs - shall and will + infinitive. Initially, we used will in all persons, except the first person singular and plural (“I” and “we”). We usually use shall for “I” and “we”. However, nowadays the English-speakers use will for all persons singular and plural. So, it will not be a great mistake if you always use will in your sentences.
- If you want to form an interrogative sentence, put shall/will at the beginning. For example:
Will you go to school tomorrow? Shall I visit the doctor next week?
- If you want to create a negative sentence, use will not = won’t; shall not = shan’t. For example:
I will not go to school tomorrow. I shall not visit the doctor next week.
USE
We use Future Simple when:
- we want to express a single action that will happen in the future. Words - indicators: tomorrow, next month, next week, soon, in two days, next year, in a year, some day, in a month. For example:
He will get married in a month. Mr. Bill will arrive next week.
- We want to express regular, repeated actions in future:
I shall visit you every week.
FORM
Future Continuous Tense is formed a bit more complicated: the auxiliary verb to be in Future Simple tense (shall be / will be) is followed by the Participle I of the main verb - -ing form. For example:
Will be writing; shall be calling; will be playing; will be cooking, etc.
- If you want to form an interrogative sentence, put shall/will at the beginning + pronoun + verb + ing. For example:
Will I be going? Will he be cooking?
- If you want to create negative a sentence, use will not be = won’t be; shall not be = shan’t be. For example:
I will not be going. He will not be cooking.
USE
We use Future Continuous Tense when:
- we want to show that the action will take place at a particular moment in the future expressed by adverbial modifier of time:
In two days, he will be teaching English at school.
- We want to predict an action in future:
My mother will be worrying about me if I do not answer her calls.
The Future Perfect Tense indicates that an action will have been finished at particular moment in the future. It is formed using shall/will + have + Past Participle of the verb (regular or irregular form).
For example:
I will have spent all my money by the end of the next month.
I will have pass exams successfully if I learn all rules.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense is used to project/ forecast actions in time. It refers to actions or events in a time between now and future that are unfinished. It is formed by using the future perfect of the verb to be (will have been) + the Present Participle of the verb + ing.
For example:
I will have been waiting her for 3 hours here tomorrow
Next year I will have been working here for four years.
Other ways of expression the Future Tense in English
1. We use Present Continuous to describe an action that was preplanned and will take place in the nearest future.
We are going to eat chicken tonight. Nick is going to the hospital tomorrow.
2. We use Present Simple to describe a scheduled action, timetable, official plans, and program.
The train arrives at 18:15. The movie starts at 20:20 tonight.
3. We also use to be going to + infinitive to express an action in the future. It shows the speaker's intention to perform or accomplish something in the future.
I am going to travel to Spain this summer. They are going to get married in September.
Applying knowledge obtained in this article, you will be able to share your plans and intentions with someone using different forms of the future tense in English. And, our Editors will be able to check how you catch on to Grammar rules: future tenses in English!
